Wanted: Flexible Shops and Open-Minded Pros
AM is more complicated than the hype implies. It needs creative people to advance its adoption in this industry.
Share






We have all read the hype: You can 3D-print anything you want. Complexity is “free” when using 3D printing. Additive manufacturing is going to put machining facilities out of business. And so on.
Anyone who has actually seen and worked in additive manufacturing—the layer-by-layer fabrication of end-use parts—quickly realizes that the hype is much different from the reality. The reality is that AM is complicated, and we need agile and flexible machining facilities, along with creative and open-minded machining professionals, to help advance the technology and spur its adoption by the industry. Here’s why:
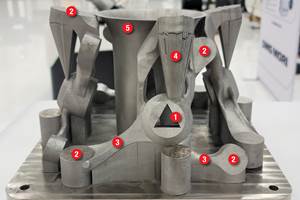
Consider the part pictured above, a component for the front suspension of a Formula SAE race car designed and built by students at Pennsylvania State University. The part is made of titanium, Ti-6Al-4V to be exact, and was designed and optimized by Vincent Maranan, an undergraduate honors student working with Dr. Todd Palmer, a colleague of mine in the materials science and engineering department. Vincent was able to use readily available design, analysis and optimization codes to lightweight the part, which was then 3D-printed on a laser-based powder-fed fusion system, a common AM process for printing fully dense metal parts.
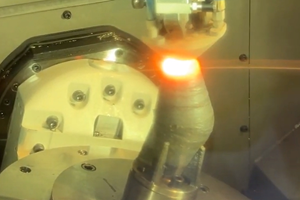
Additively manufacturing this intricate geometry is relatively easy. The machine does not care whether it is “printing” a solid part or a complex lattice; it just tells the laser where to melt the material (a very fine powder in the case of powder-bed fusion systems) so that it solidifies into a solid part. There are numerous caveats, as one might guess, and the most important one—and perhaps the most relevant to readers interested in AM—is the use of support structures to ensure a successful build.
Because the part is being fabricated layer by layer, the heating and cooling of the metal in each layer can cause the part to distort and the ends to warp up (like a potato chip) if overhanging geometries are not properly supported. As a result, you end up having to print the same part with nearly two dozen support structures and in the orientation illustrated in the second image above. Those new to AM often fail to realize that these support structures are fabricated from the same material as the part (titanium, in this case), as current powder-bed fusion systems are limited to a single material. This means large sections of the part need to be removed before end use. The current solution? Clamp the part in a vice and cut, file, grind and hack away the support structures. Not a very advanced solution for post-processing and finishing a lightweight part made with advanced AM technology.
Support removal provides numerous challenges for post-processing and machining: separation of the part and supports from the build plate; establishing datums and reference points for the part for machining; access and clearances to some areas of the structure; and fixturing and workholding in the necessary orientations, to name just a few. This is where AM gets complicated and the reality is different from the hype. Only agile and flexible machining facilities and practices, along with creative and open-minded machining professionals, will be up to the task.
Related Content
Machine Tool Drawbar Made With Additive Manufacturing Saves DMG MORI 90% Lead Time and 67% CO2 Emission
A new production process for the multimetal drawbar replaces an outsourced plating step with directed energy deposition, performing this DED along with roughing, finishing and grinding on a single machine.
Read MoreDesigning a 3D Printed Part with Machining in Mind
Designing extra stock and mounting features into a 3D printed part can aid in machining processes downstream.
Read MoreAdditive/Subtractive Hybrid CNC Machine Tools Continue to Make Gains (Includes Video)
The hybrid machine tool is an idea that continues to advance. Two important developments of recent years expand the possibilities for this platform.
Read MoreChuck Jaws Achieve 77% Weight Reduction Through 3D Printing
Alpha Precision Group (APG) has developed an innovative workholding design for faster spindle speeds through sinter-based additive manufacturing.
Read MoreRead Next
Last Chance! 2025 Top Shops Benchmarking Survey Still Open Through April 30
Don’t miss out! 91ÊÓƵÍøÕ¾ÎÛ's Top Shops Benchmarking Survey is still open — but not for long. This is your last chance to a receive free, customized benchmarking report that includes actionable feedback across several shopfloor and business metrics.
Read MoreMachine Shop MBA
Making Chips and 91ÊÓƵÍøÕ¾ÎÛ are teaming up for a new podcast series called Machine Shop MBA—designed to help manufacturers measure their success against the industry’s best. Through the lens of the Top Shops benchmarking program, the series explores the KPIs that set high-performing shops apart, from machine utilization and first-pass yield to employee engagement and revenue per employee.
Read MoreAMRs Are Moving Into Manufacturing: 4 Considerations for Implementation
AMRs can provide a flexible, easy-to-use automation platform so long as manufacturers choose a suitable task and prepare their facilities.
Read More