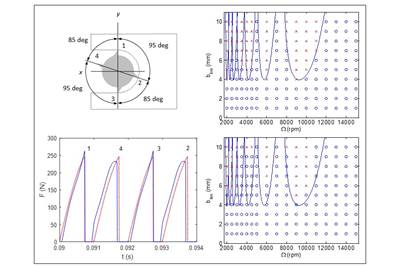
Milling Tools
Milling is a complex metal removal process that usually involves a clamped workpiece being fed in a linear direction into a multiple tooth rotating cutter. Due to the vast variety of machinery, controls and tools that are available, milling is one of the universal machining methods of choice. It offers excellent machining efficiency, good surface finishes, great flexibility and a high degree of accuracy. While turning is frequently used to create round surfaces with a single cutting edge, milling normally uses several cutting edges in a single tool to create flat faces, shoulders, slots and contoured surfaces. There are many types of machine tools used to perform a milling operation, including manually controlled, numerically controlled and special dedicated machines.






ESSENTIAL READING
VIEW ALL10 Tips for Titanium
Simple process considerations can increase your productivity in milling titanium alloys.
Read MoreA New Milling 101: Milling Forces and Formulas
The forces involved in the milling process can be quantified, thus allowing mathematical tools to predict and control these forces. Formulas for calculating these forces accurately make it possible to optimize the quality of milling operations.
Read MoreHow to Tackle Tough Angled Pocket Milling With Two Tools
Milling a deep pocket with a tight corner radius comes with unique challenges, but using both a flat bottom drill and a necked-down finishing tool can help.
Read MoreChoosing Your Carbide Grade: A Guide
Without an international standard for designating carbide grades or application ranges, users must rely on relative judgments and background knowledge for success.
Read MoreHow to Manage Cutting Tool Inventory in a Small Job Shop — The One-Person Shop #4
Working in short lead times means maintaining a large range of tools to be ready. What is the right way to stock and organize this investment?
WatchWhy Binderless CBN Inserts Turn Titanium Faster
A new formulation of cubic boron nitride could provide a more solid alternative to cemented carbide as finish-machining becomes more demanding.
Read MoreLatest Milling Tools News And Updates
Engis Milling Tool Enables High Stock Removal Rates
PMTS 2025: The Engis ElectroMill is designed to produce high-quality, flat milled surfaces, even if an interrupted cut is present or multiple materials need to be machined simultaneously.
Read MoreTungaloy Milling Tool Features Extra-Close Pitch Cutters
The TungSpeed-Mill series features a lightweight construction and the necessary strength for challenging automotive and general industrial machinery applications.
Read MoreIMCO End Mills Enable Aggressive Cutting Action
Pow-R-Feed M934 cutters feature fine cutting edges with optimal strength, plus a wiper flat end for smooth floor finishes.
Read MorePicking the Right End Mill
Kennametal global product manager Katie Myers explains how cutting tool features can impact machining strategies for different materials.
Read MoreTungaloy Milling Tool Provides Enhanced Edge Strength
The MillQuadFeed cutting tool features a specialized insert geometry that is said to reduce cutting resistance by up to 20%, enhancing machining efficiency.
Read MoreSimtek Milling Tool Features Monoblock Performance Features
The SimMill 9W4 tool milling system is designed to work precisely and stably under difficult conditions, such as in limited space with long overhang lengths.
Read MoreFeatured Posts
Shoulder Milling Cuts Racing Part's Cycle Time By Over 50%
Pairing a shoulder mill with a five-axis machine has cut costs and cycle times for one of TTI Machine’s parts, enabling it to support a niche racing community.
Read MoreThe Impact of Cutting Teeth Spacing on Machining Stability
Many cutter designs are available, and variable teeth spacing (or variable pitch) cutters can be used to influence milling stability. Let’s discuss why teeth spacing affects stability.
Read MoreGrooving Attachment Streamlines Operation by 75%
A grooving attachment enabled Keselowski Advanced Manufacturing to reduce cycle times by over 45 minutes on a high-value, high-nickel part feature.
Read MoreTwin Spindle Design Doubles Production of Small Parts
After experiencing process stalls in the finishing stage of production, Bryan Machine Service designed an air-powered twin spindle and indexable rotating base to effectively double its production of small parts.
Watch10 Tips for Titanium
Simple process considerations can increase your productivity in milling titanium alloys.
Read MoreA New Milling 101: Milling Forces and Formulas
The forces involved in the milling process can be quantified, thus allowing mathematical tools to predict and control these forces. Formulas for calculating these forces accurately make it possible to optimize the quality of milling operations.
Read MoreFAQ: Milling Tools
What is milling?
At its most basic, milling is the meeting of a rotating tool with a clamped and stationary workpiece, as opposed to turning where the tool is stationary and the work material rotates. Actually, the workpiece has feed motion imparted from the machine tool. The meeting of the rotary motion of the cutter and the cutting edge of the tools produces fluctuating cutting forces: vibration, heat, and, if all goes well, chips.
Source: A New Milling 101: What Milling Is, Then and Now (Plus a Glossary of Milling Terms)
What is a milling machine?
Milling machines may have either vertical or horizontal spindle orientation, and typically, face milling cuts flat surfaces, but multi-axis CNC machines make it possible to include three-dimensional movements. That said, there are four basic categories of milling: face milling, periphery milling, slot milling, and specialty applications.
Source: A New Milling 101: What Milling Is, Then and Now (Plus a Glossary of Milling Terms)
What are the basic categories of milling?
Face milling: Used for creating a flat surface (face) on the workpiece. The cutting plane is usually perpendicular to the axis of rotation and the cutters most often feature a single row of inserts, designed with a wide range of cutting geometries, inserts, lead angles, and mounting adaptations.
Periphery milling: Generates a primary surface parallel to the spindle rotation. A secondary surface is sometimes produced. The cutting plane is usually parallel to the axis of rotation.
Slot milling: Used for producing a slot or channel in the workpiece. There are two primary types of slot milling cutters: disk mills and end mills. Disk mills can be high-speed steel, brazed carbide, and indexable-insert-based. They are typically used in operations perpendicular to the spindle rotation.
Specialty applications: Includes copy milling, plunge milling, ramping, helical and circular interpolation, trochoidal, and others.
Source: A New Milling 101: What Milling Is, Then and Now (Plus a Glossary of Milling Terms)